Cashew Conundrum - Discovering Its Fruit and Nut Nature
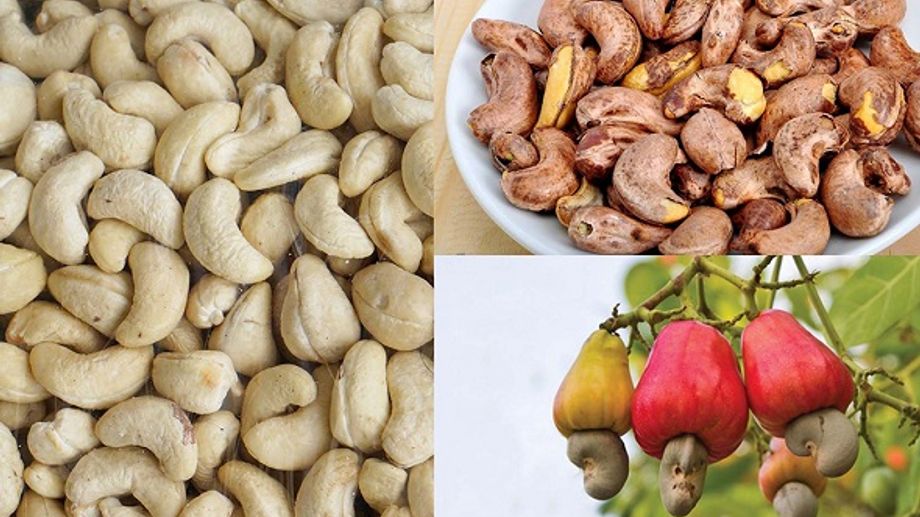

1. Cashew is a fruit or seed
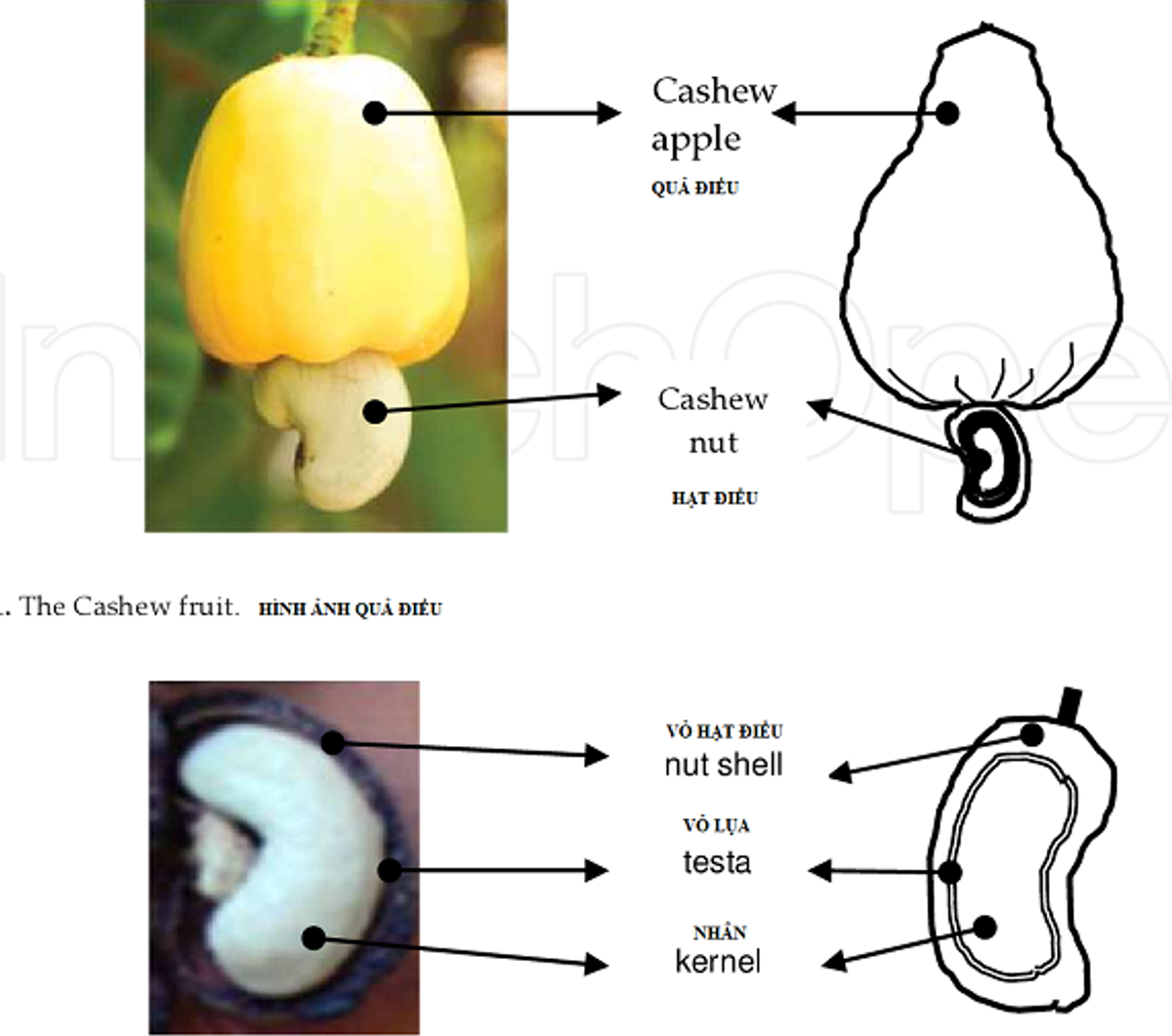
The cashew is actually both! It consists of two main parts: the cashew apple and the cashew nut.
Cashew Apple
- Fruit Part: The cashew apple is the fleshy, pear-shaped structure that grows from the stem of the cashew tree. It's typically yellow, red, or orange and has a sweet-tart flavor. It's rich in Vitamin C and can be eaten fresh or used to make juices, jams, and alcoholic beverages.
Cashew Nut
- Seed Part: The cashew nut is the seed of the cashew apple and grows at the bottom of the fruit, encased in a hard shell containing toxic resin called urushiol. The nut is carefully processed to remove the shell and resin, making it safe to eat. Once processed, the cashew nut is used in a variety of culinary applications, from raw and roasted snacks to cashew butter and milk.
So, the cashew is a unique combo of both fruit and seed, each part offering different benefits and uses.
2. Full explanation about cashew fruit
Cashew fruits are fascinating and unique, consisting of two distinct parts: the cashew apple and the cashew nut.
Cashew Apple
- Description: The cashew apple is the fleshy, pear-shaped structure that grows from the stem of the cashew tree. It's usually yellow, red, or orange in color.
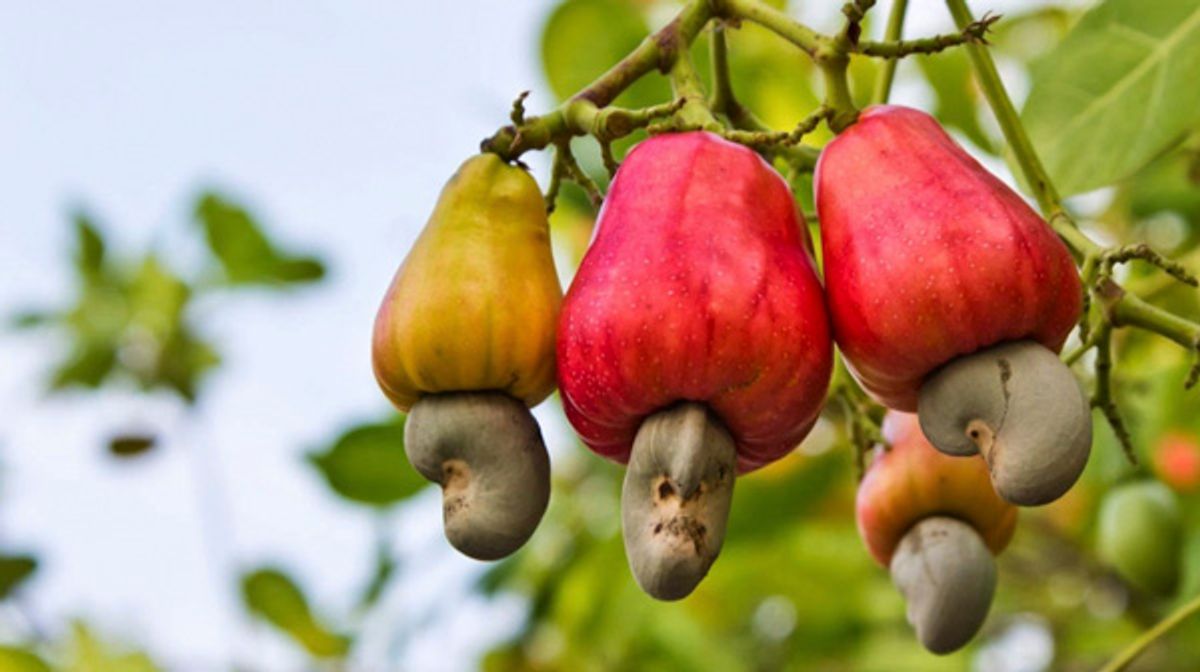

- Taste and Texture: The cashew apple has a juicy, fibrous texture and a slightly sweet to tart flavor. It's rich in vitamins, especially Vitamin C, and has a refreshing taste.
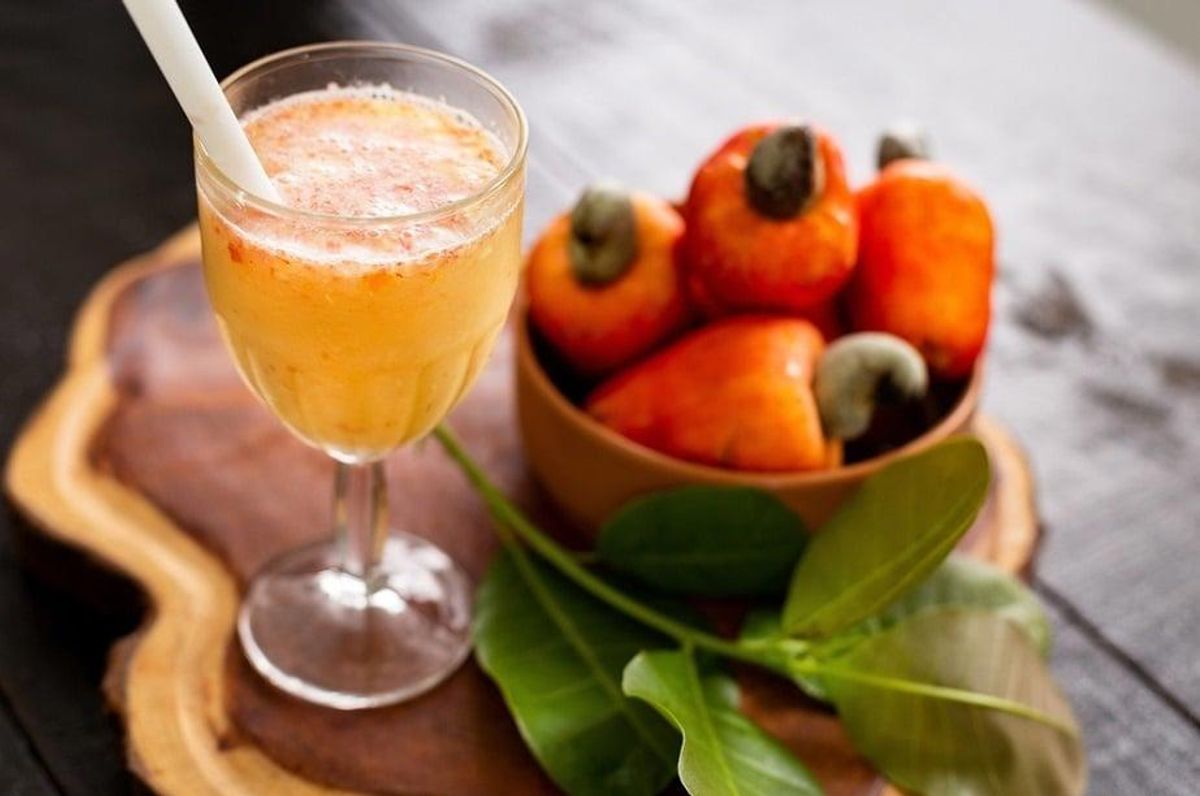
- Usage: While not as well-known as the cashew nut, the cashew apple is consumed in many cashew-growing regions. It can be eaten fresh or used to make juices, jams, and alcoholic beverages like cashew wine and feni (a popular spirit in Goa, India).

Nutritional Benefits
- Cashew Apple: Rich in Vitamin C, antioxidants, and fiber, the cashew apple is excellent for boosting immunity, improving digestion, and providing hydration.
- Cashew Nut: High in healthy fats, protein, vitamins, and minerals, cashews are beneficial for heart health, weight management, and overall wellness.
Economic Importance
- Global Market: Cashews are a significant export product for many tropical countries. Major producers include Vietnam, India, Brazil, and Nigeria.
- Local Economy: In many cashew-growing regions, both the cashew apple and the nut are vital for local economies, providing income for farmers and workers involved in cultivation and processing.
Conclusion
The cashew fruit is a remarkable example of nature's bounty, offering both the cashew apple and the nut, each with its own unique benefits and uses. From the nutritious juice of the cashew apple to the versatile and tasty cashew nut, this fruit is a valuable resource in many parts of the world.
3. Nutritional composition of cashew fruit
The cashew fruit, which includes both the cashew apple and the cashew nut, is packed with essential nutrients. Here's a detailed look at its nutritional composition:
Cashew Apple
- Vitamins: Rich in Vitamin C, which boosts immunity and skin health.
- Minerals: Contains potassium, magnesium, and iron, which are vital for muscle function, bone health, and oxygen transport.
- Fiber: High in dietary fiber, aiding in digestion and promoting a healthy gut.
- Antioxidants: Contains various antioxidants that help combat oxidative stress and inflammation.
Cashew Nut
- Healthy Fats: High in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which are beneficial for heart health.
- Protein: Good source of plant-based protein, essential for muscle repair and growth.
- Minerals: Rich in copper, magnesium, zinc, and phosphorus, supporting various bodily functions.
Vitamins: Contains B vitamins (B1, B6, B5), Vitamin K, and small amounts of Vitamin E and C.
Overall Nutritional Benefits
- Heart Health: The healthy fats in cashews can help lower bad cholesterol levels and improve heart health.
- Weight Management: The fiber content helps in feeling full, which can aid in weight management.
- Bone Health: Magnesium and calcium contribute to strong bones and teeth.
- Energy Boost: The combination of carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats provides a steady source of energy.
Cashew fruits are not only nutritious but also versatile in culinary uses, from fresh consumption to juices, jams, and nut-based products.
4. Full explanation about cashews
Cashews are an incredibly versatile and nutritious food that holds a unique place in both culinary and agricultural worlds. Here's a full overview:
The Cashew Tree
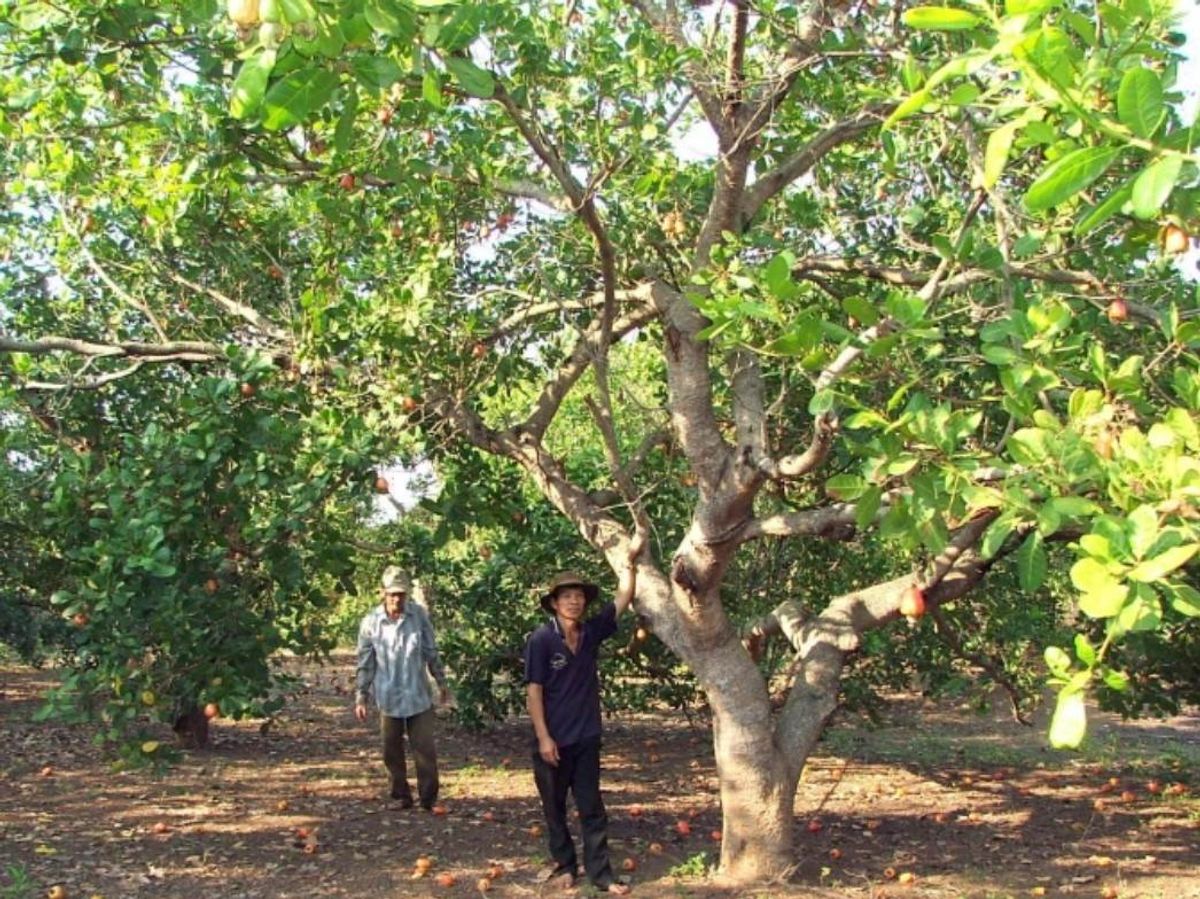

- Origin: Cashews (Anacardium occidentale) originate from Brazil but are now widely cultivated in tropical regions across the globe, including Vietnam, India, and parts of Africa.
- Tree Structure: Cashew trees are evergreen, growing up to 14 meters tall, with broad leaves and flowers that develop into cashew apples and nuts.
Cashew Fruit and Nut
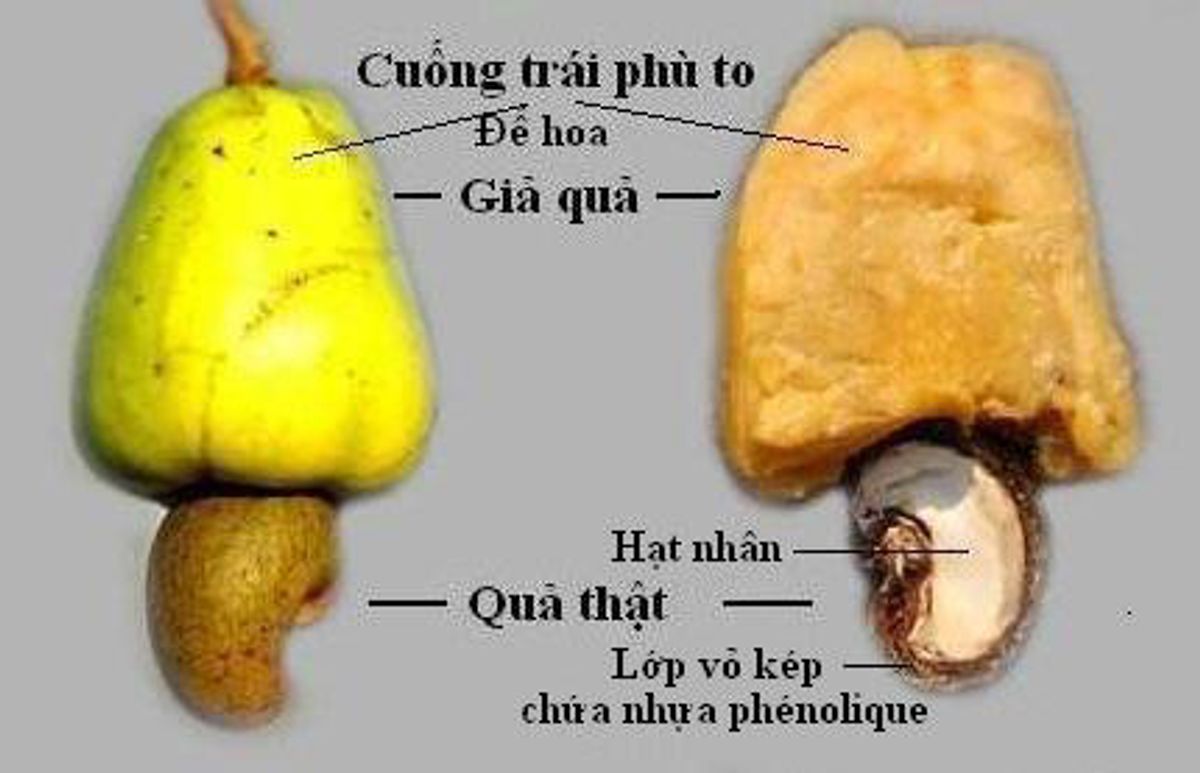
- Cashew Apple: This is the fleshy part of the cashew fruit, usually pear-shaped and varying in color from yellow to red. It has a juicy, sweet-tart flavor and is rich in Vitamin C.
- Uses: Cashew apples are often used in juices, jams, and fermented to make alcoholic beverages like cashew wine and feni.
- Cashew Nut: The true seed of the cashew fruit, it grows at the bottom of the cashew apple, encased in a double-layered shell that contains toxic resin.
- Processing: Requires careful steaming or roasting to neutralize the toxins before the shells are removed. This meticulous process is necessary to make cashews safe for consumption.
Nutritional Composition
Cashew Nuts:
- Healthy Fats: High in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats beneficial for heart health.
- Protein: A good source of plant-based protein.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Rich in magnesium, copper, zinc, and phosphorus.
- Calories: Dense in calories, making them a good energy source but also something to enjoy in moderation.
Cashew Apples:
- Vitamin C: Extremely high in Vitamin C, providing immune support.
- Fiber: Contains dietary fiber that aids in digestion.
- Antioxidants: Packed with antioxidants that help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress.
Culinary Uses
- Raw or Roasted: Cashews can be consumed raw or roasted, with or without salt.
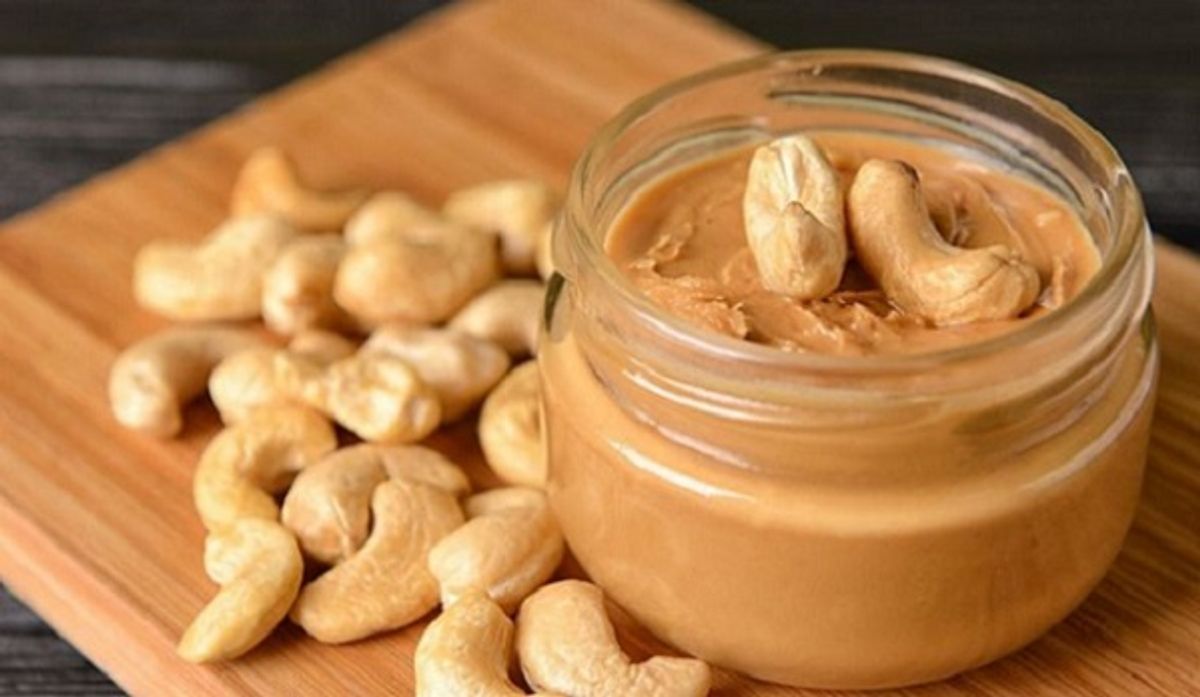
- Cashew Butter: Made from ground cashews, used as a spread similar to peanut butter.

- Cashew Milk: A dairy-free alternative to milk, made from cashews blended with water.
- Cashew Cheese: A vegan cheese alternative made using cashews.

- Culinary Ingredient: Widely used in cooking and baking, adding texture and flavor to dishes, especially in Asian and Indian cuisines.
Economic Importance
- Global Market: Cashews are a significant agricultural export for many tropical countries. Major producers include Vietnam, India, Brazil, and Nigeria.
- Local Economy: Provides income and employment in many rural areas. The entire production process from cultivation to processing involves many hands, contributing to local economies.
Health Benefits
- Heart Health: The healthy fats in cashews can help reduce bad cholesterol and improve overall heart health.
- Bone Health: Rich in magnesium and phosphorus, essential for healthy bones and teeth.
- Weight Management: High in protein and fiber, which can help keep you full and aid in weight management.
- Skin Health: The copper content supports collagen production, which can benefit skin health.
Environmental Impact
- Sustainability: While cashew farming can be sustainable, it requires careful water management and responsible farming practices to avoid deforestation and depletion of natural resources.
- Challenges: The process of harvesting and processing cashews is labor-intensive and sometimes linked to poor working conditions. Supporting fair trade cashews ensures ethical sourcing and better conditions for workers.
Conclusion
Cashews are much more than just a tasty snack; they're a powerhouse of nutrients and play a vital role in global agriculture and economies. Their journey from tree to table is complex and involves many steps to ensure they are safe and delicious.
5. Nutritional composition of cashew nuts
Cashew nuts are not only delicious but also packed with essential nutrients. Here's a detailed breakdown of their nutritional composition:
Macronutrients
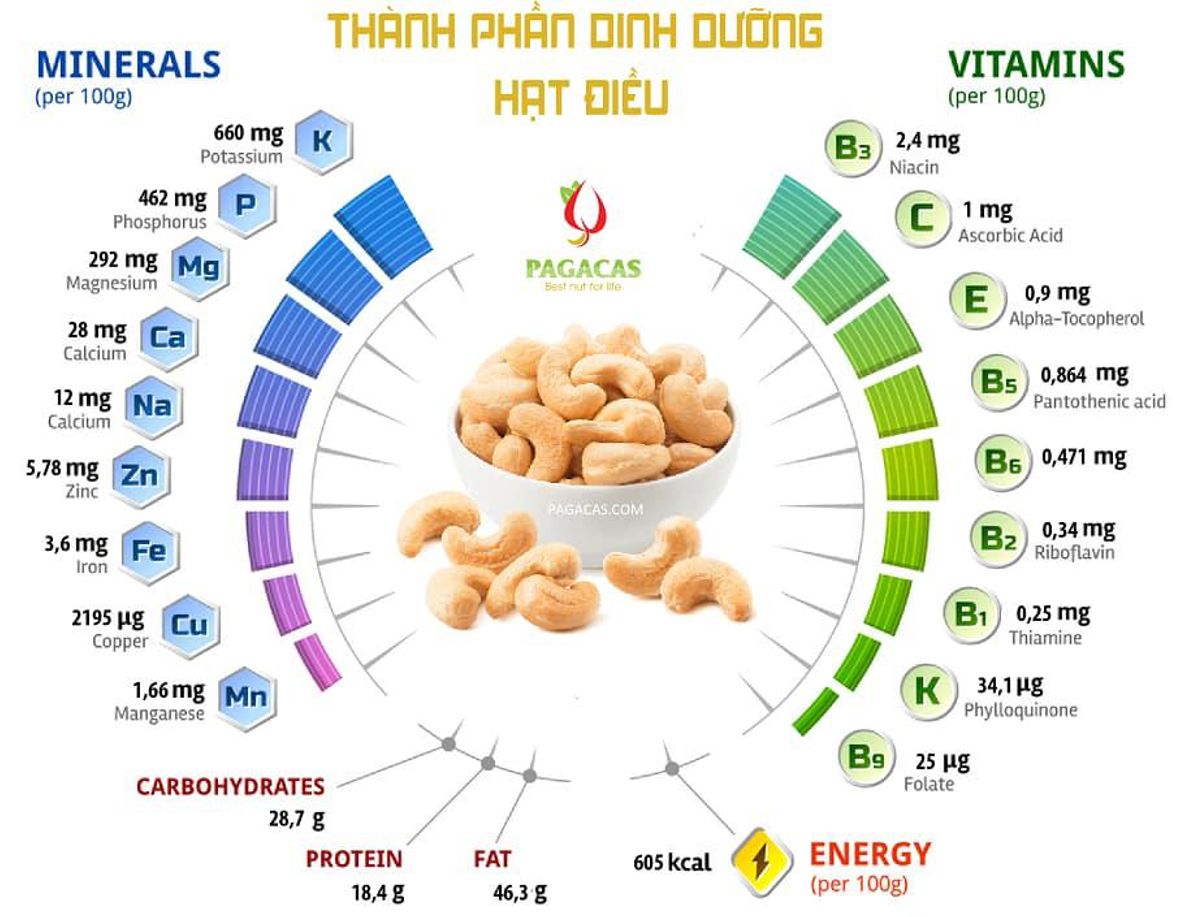
- Calories: Approximately 553 calories per 100 grams.
- Protein: Around 18.2 grams per 100 grams, providing a good source of plant-based protein.
- Fats: Roughly 44.4 grams per 100 grams, including:
- Monounsaturated fats: 23.8 grams
- Polyunsaturated fats: 7.8 grams
- Saturated fats: 7.8 grams
- Carbohydrates: About 30.2 grams per 100 grams, including:
- Dietary fiber: 3.3 grams
- Sugars: 5.9 grams
Micronutrients
Vitamins:
- Vitamin E: 0.9 mg
- Vitamin K: 34.1 µg
- Vitamin B6: 0.3 mg
- Thiamine (Vitamin B1): 0.4 mg
- Riboflavin (Vitamin B2): 0.1 mg
- Niacin (Vitamin B3): 1.1 mg
- Folate: 25 µg
Minerals:
- Magnesium: 292 mg
- Phosphorus: 593 mg
- Iron: 6.7 mg
- Potassium: 660 mg
- Zinc: 5.8 mg
- Copper: 2.2 mg
- Selenium: 19.9 µg
Health Benefits
- Heart Health: The monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats help reduce bad cholesterol levels and improve heart health.
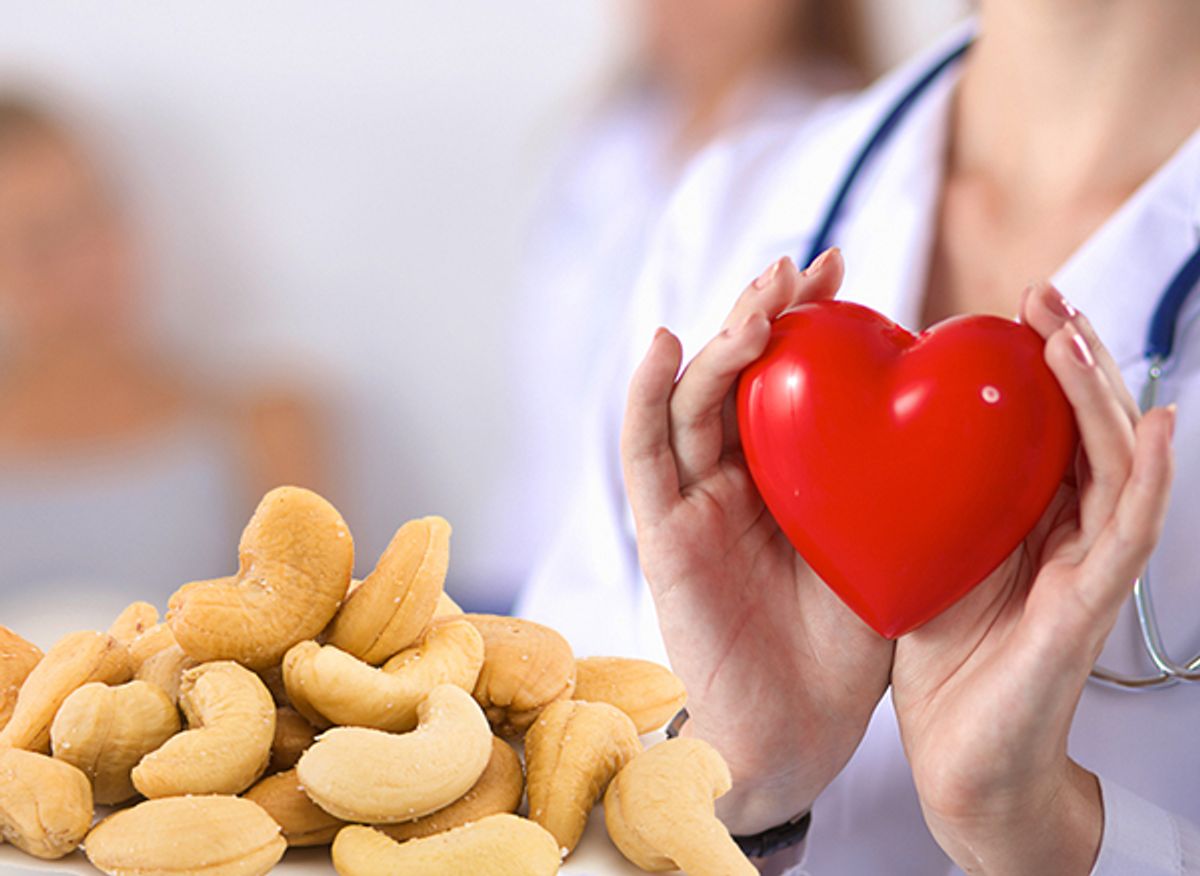

- Bone Health: High levels of magnesium and phosphorus support strong bones and teeth.
- Antioxidant Properties: Vitamins E and K, along with other antioxidants, help combat oxidative stress and inflammation.
- Energy Boost: The combination of protein, healthy fats, and carbohydrates provides a steady source of energy.
Cashews are a nutritional powerhouse, making them an excellent addition to a balanced diet. They're perfect for snacking, cooking, and even making dairy-free alternatives like cashew milk and cheese.
Xem thêm: Điều là quả hay hạt? Giải thích đấy đủ về quả điều và hạt điều
Learn more: Are Cashews Seeds, Fruits or Nuts? Characteristics of Cashews & Cashew Nuts