Net Carbs in Cashews - What You Need to Know

1. Do cashews contain net carbs? How much net carbs are in cashews?
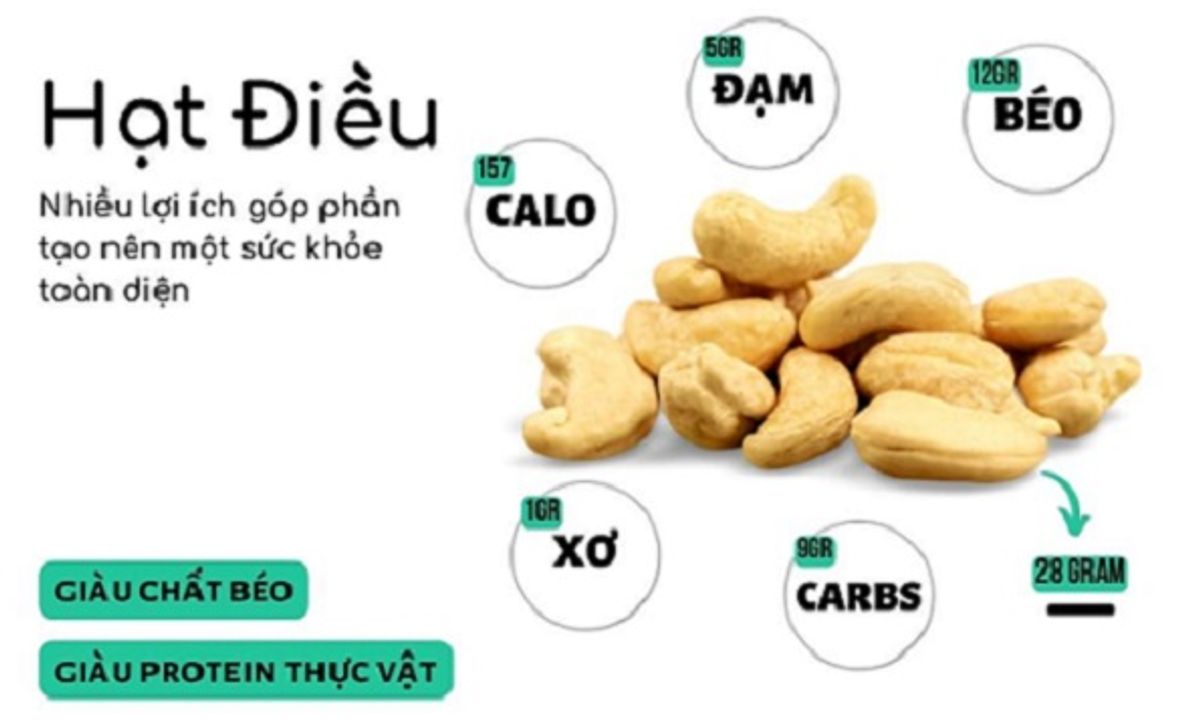
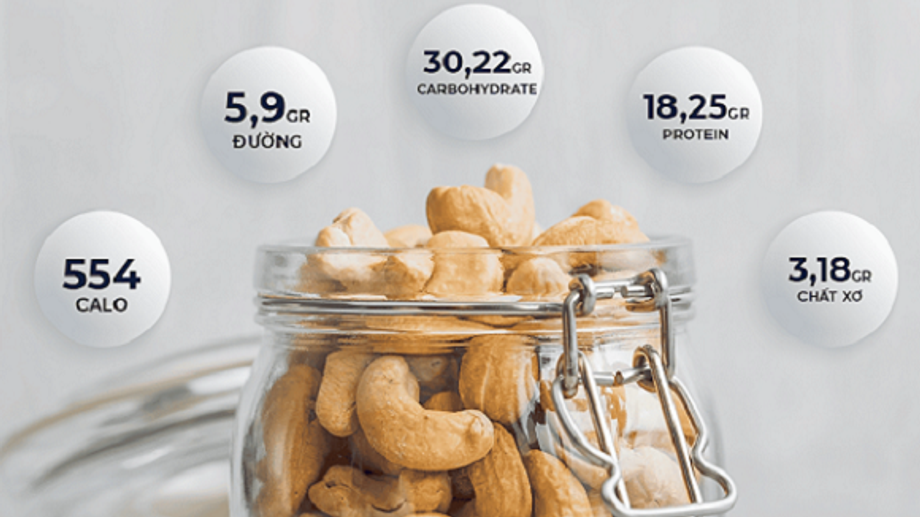
Cashews do contain net carbs. For a 1-ounce (28-gram) serving of raw cashews, there are approximately 8.5 grams of total carbs and 0.9 grams of fiber, which results in about 7.6 grams of net carbs.
Keep in mind that portion control is important, especially if you're following a low-carb or keto diet. Enjoying cashews in moderation can help you manage your carb intake while still benefiting from their nutritional value.
2. What Are Net Carbs? Types of net carbs in cashews

Net carbs are the total amount of carbohydrates in a food minus the fiber content. The idea behind net carbs is that fiber, which is a type of carbohydrate, is not digested and absorbed by the body in the same way as other carbs, so it doesn't contribute to blood sugar levels. Therefore, net carbs give a more accurate representation of the carbs that impact blood sugar and insulin levels.
Types of Net Carbs in Cashews
Cashews contain different types of carbohydrates, but when calculating net carbs, we primarily focus on the digestible carbs:
- Total Carbohydrates: This is the sum of all types of carbs in cashews, including sugars, fiber, and starches.
- Dietary Fiber: This type of carbohydrate is not bsorbed by the body and does not impact blood sugar levels. It is subtracted from the total carbs to get net carbs.
- Sugars: These are the natural sugars present in cashews, which are digestible and contribute to the net carbs.
- Starches: These complex carbs break down into sugars during digestion and are included in the net carbs.
For a 1-ounce (28-gram) serving of raw cashews, there are approximately:
- 8.5 grams of total carbs
- 0.9 grams of dietary fiber
- This results in:
- 7.6 grams of net carbs (total carbs minus fiber)
Understanding net carbs is particularly important for individuals following low-carb or ketogenic diets, where managing carbohydrate intake is crucial. Cashews, while nutritious, should be consumed in moderation within such dietary plans to ensure you stay within your net carb limits.
3. Effects of Net Carbs on the Body
Net carbs have significant impacts on the body, particularly on blood sugar levels, energy, and overall health. Here's a closer look at how net carbs affect the body:
Blood Sugar Levels
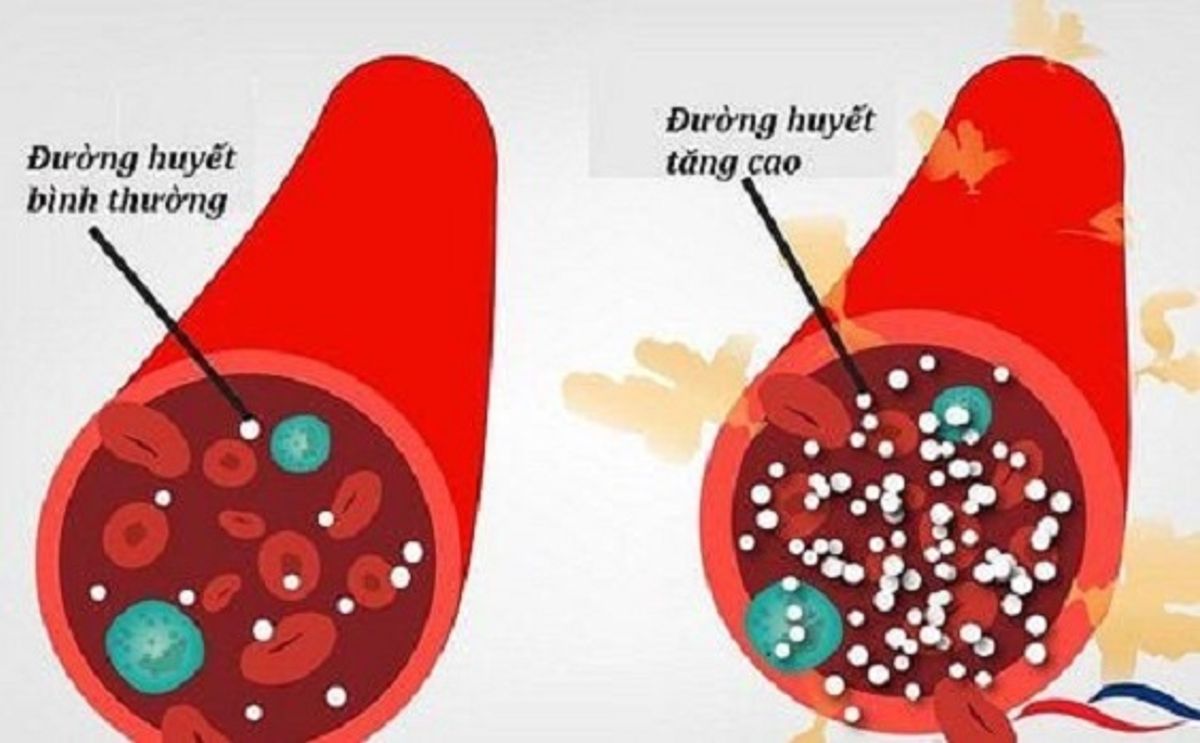
- Increases Blood Sugar: Net carbs, especially sugars and starches, are broken down into glucose during digestion, which enters the bloodstream and raises blood sugar levels.
- Insulin Response: The increase in blood sugar triggers the release of insulin, a hormone that helps cells absorb glucose for energy or store it as fat.
Energy Levels
- Immediate Energy Source: Net carbs provide a quick and immediate source of energy. Foods high in net carbs can boost energy levels rapidly, which is why they are often consumed before or after physical activity.
- Sustained Energy: Complex carbs, which are part of net carbs, break down more slowly and provide a more sustained and steady release of energy over time.
Weight Management
- Calorie Intake: Net carbs contribute to the total calorie intake. Consuming high amounts of net carbs without burning them off can lead to weight gain.
- Satiety: Fiber, which is subtracted from total carbs to calculate net carbs, aids in feeling full longer, which can help with weight management by reducing overall calorie intake.
Digestive Health
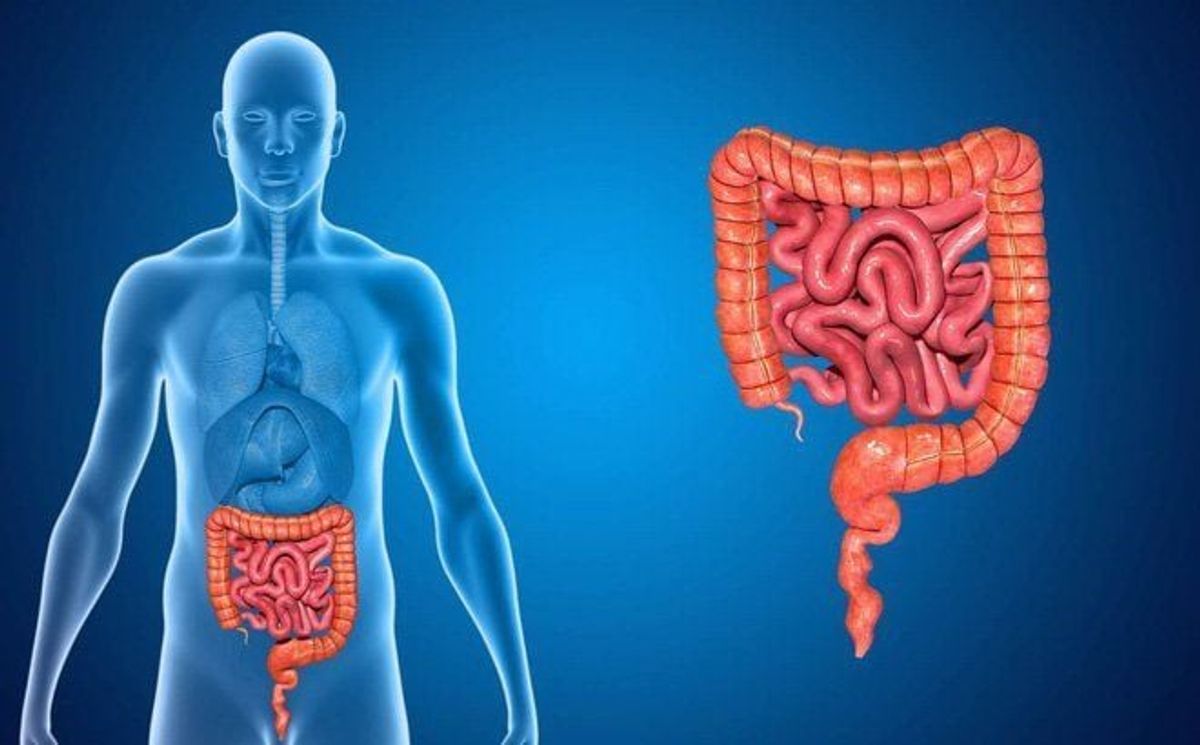
- Gut Health: Fiber, though not contributing to net carbs, plays a crucial role in digestive health by promoting regular bowel movements and supporting the growth of healthy gut bacteria.
Metabolic Health
- Insulin Sensitivity: Consuming a balanced amount of net carbs can improve insulin sensitivity, which is important for metabolic health. However, excessive intake can lead to insulin resistance and increase the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Fat Storage: Excess glucose from high net carb intake can be stored as fat, contributing to weight gain and potentially leading to metabolic disorders.
Cardiovascular Health
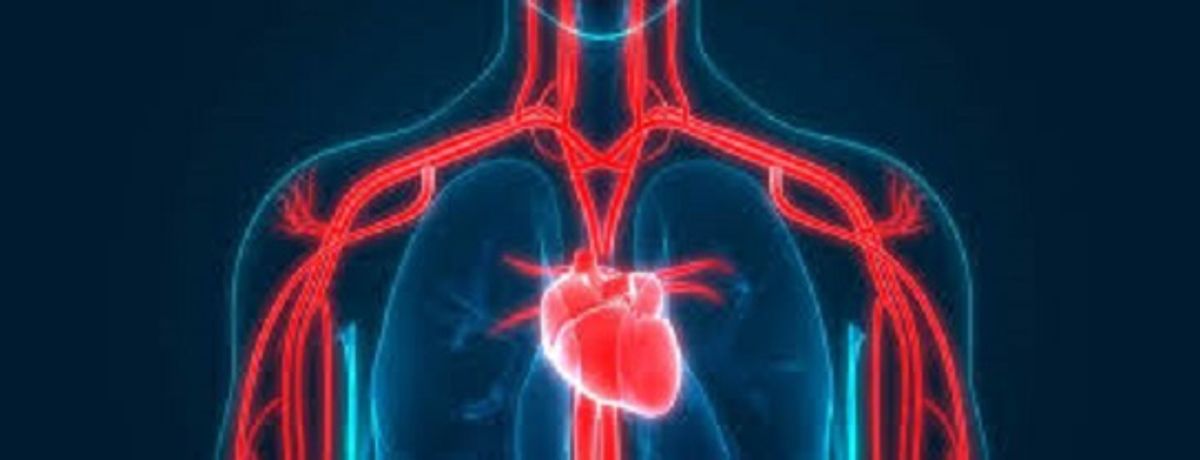
- Blood Lipid Levels: Diets high in simple sugars (a component of net carbs) can negatively impact blood lipid levels, increasing the risk of heart disease. On the other hand, a balanced intake of complex carbs can support cardiovascular health.
Conclusion
Net carbs have a range of effects on the body, from influencing blood sugar levels and energy to impacting weight management and overall health. Managing net carb intake, particularly by choosing complex carbs and fiber-rich foods, can help maintain a balanced diet and support long-term health goals. If you're mindful of your net carb intake, you can enjoy foods like cashews in moderation while still reaping their nutritional benefits.
4. How should cashews be used with your diet to supplement the appropriate amount of net carbs?
Incorporating cashews into your diet can be a great way to get a healthy dose of nutrients while managing your net carb intake. Here’s how you can use cashews effectively:
Portion Control
- Serving Size: Stick to a small serving size, such as 1 ounce (28 grams) of cashews, which contains around 7.6 grams of net carbs. This helps keep your net carb intake in check.
- Measure Portions: Use a kitchen scale or measuring cups to ensure you’re eating the right amount.
Balance with Other Foods
- Combine with Protein: Pair cashews with protein-rich foods like Greek yogurt, lean meats, or cheese to create a balanced snack that keeps you fuller for longer.

- Include Fiber-Rich Foods: Combine cashews with fiber-rich veggies or whole grains to improve digestion and control blood sugar levels.
Use as a Snack
- Healthy Snacking: Enjoy a small handful of cashews as a mid-morning or afternoon snack to keep your energy levels stable without overloading on carbs.

- Mix with Other Nuts: Create a mix of nuts including cashews, almonds, and walnuts to diversify nutrients and avoid consuming too many net carbs from one source.

Add to Meals
- Salads: Sprinkle cashews over salads for a crunchy texture and nutty flavor.
- Stir-Fries: Add cashews to stir-fries with plenty of vegetables and lean protein for a balanced, nutrient-dense meal.

- Oatmeal or Smoothies: Blend cashews into oatmeal or smoothies for a creamy texture and added protein.
Cooking with Cashews
- Cashew Butter: Use cashew butter as a spread on whole grain toast or as a dip for fruits and veggies. Remember to account for the net carbs in the serving size.
- Sauces: Blend cashews into sauces for a creamy, dairy-free alternative that adds healthy fats and a touch of sweetness.
Be Mindful of Added Ingredients
- Avoid Sugary Coatings: Choose plain, unsalted cashews over those with added sugars or flavorings to keep your net carb intake lower.
- Watch for Added Oils: Be cautious with cashews that have added oils, as they can increase the calorie content without providing additional nutrients.
In Summary
Cashews can be a nutritious and tasty addition to your diet, provided you manage portions and balance them with other nutrient-rich foods. This approach helps you enjoy the benefits of cashews while keeping your net carb intake in check. Enjoy your cashews in moderation and get the most out of their nutritional goodness!
Xem thêm: Hạt điều có chứa net carbs không? Lượng net carbs trong hạt điều là bao nhiêu
Learn more: Do Cashews Contain Net Carbs? How Many Net Carbs Are in Cashews?